I. The Challenge: Making a “Basic” Ceiling Light Smart
Recently, I replaced my living room ceiling light with a new model. This light supports both remote and mobile app control, making it appear smart. However, it lacks integration with Mi Home or HomeKit. After research, I discovered that the premium version of the same brand supports Mi Home control, while my basic version doesn’t - a price difference of approximately 100 RMB.
As a developer, I approached this from first principles: Since the mobile app requires Bluetooth permissions, it must use Bluetooth for communication. If it’s Bluetooth-controlled, it can theoretically be controlled by other Bluetooth applications and integrated into smart home ecosystems.
Note: For those interested in implementing this solution, refer to my detailed tutorial: Tutorial: Make Your Non-Smart Bluetooth Light Work with HomeKit
Current State Demonstration
To view the final implementation, click here to jump.
II. Exploration: Home Assistant and Bluetooth Control Solutions
I began researching potential solutions. Since direct Mi Home integration wasn’t possible, I explored alternative approaches. This led me to discover Home Assistant (HA).
Open source home automation that puts local control and privacy first. Powered by a worldwide community of tinkerers and DIY enthusiasts.
I discovered that Home Assistant includes a HomeKit Bridge component that can bridge various non-HomeKit devices to HomeKit. This opened up new possibilities.
Further research in the Home Assistant community led me to ha-ble-adv, a solution specifically designed for Bluetooth integration.
- Home Assistant Bluetooth Low Energy Advertisement
- HA Custom Integration to control BLE ADV Ceiling Fans / Lamps
- Integration of Bluetooth controlled ceiling lamp
- Convert a “smart” chinese lamp to a real smart lamp
- Controlling BLE ceiling light with HA
This led to a clear implementation plan:
- Control the Bluetooth light via
ha-ble-adv - Manage
ha-ble-advthroughHome Assistant - Integrate with HomeKit using
Home Assistant’sHomeKit Bridge
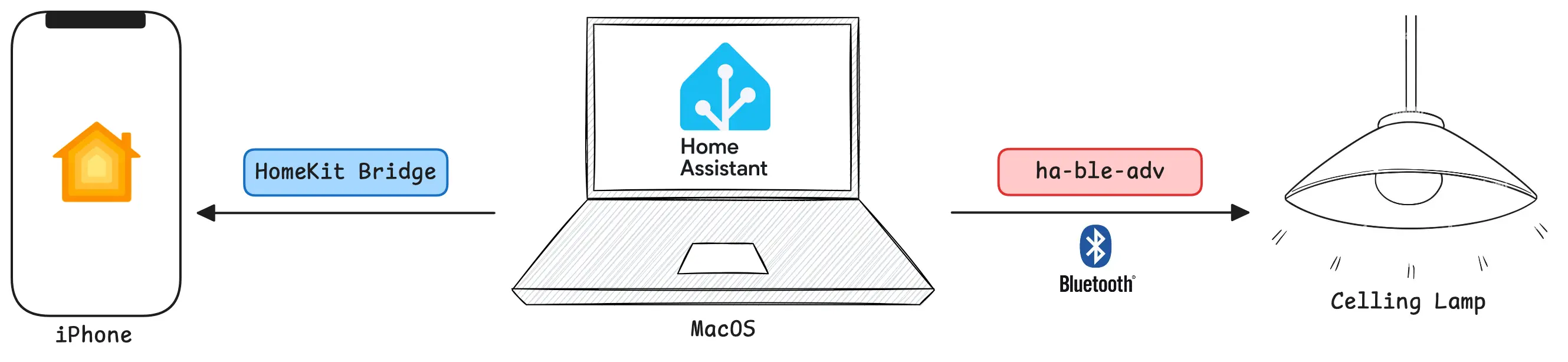
III. Implementation: Docker Environment Challenges
With the theory validated, I began implementation. I started by setting up Home Assistant:
- Install
Home Assistant - Install
Home AssistantCommunity Store (HACS) - Install
ha-ble-advvia HACS
The first challenge emerged when attempting to connect the Bluetooth light: Bluetooth adapter not found.
Research revealed that Home Assistant running in Docker cannot access host machine’s Bluetooth devices. Most tutorials focus on Linux environments.
I found a solution:
Easiest way to handle bluetooth (basically regardless of how you’re running HA) is to use an ESPHome BT proxy. Spend $5 on a ESP32, flash the BT proxy firmware, and you magically have bluetooth connectivity wherever you place your ESP(s) – Reddit: Is bluetooth possible for docker in Mac?
Additionally, ha-ble-adv doesn’t support native macOS Bluetooth devices, as documented in this issue.
I purchased an ESP32 board for 25 RMB as the simplest solution.
3.1 Initial ESP32 Setup: Wi-Fi Configuration
I began configuring the ESP32. The ha-ble-adv documentation recommended using esphome-ble_adv_proxy as the Bluetooth proxy.
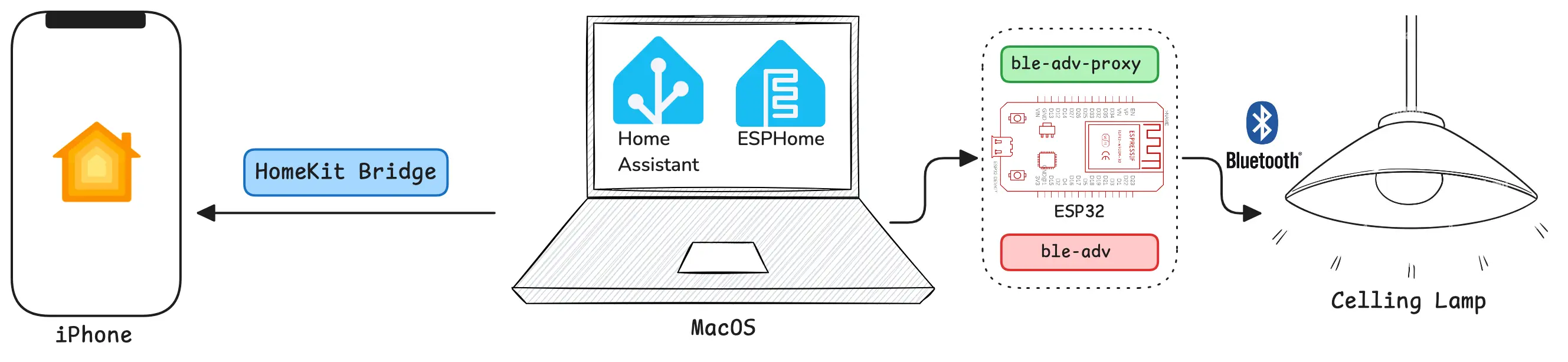
Following the documentation:
- Install ESPHome for
ESP32configuration andHome Assistantintegration - Connect the
ESP32board via ESPHome - Flash the
ble_adv_proxycomponent
The second challenge appeared: Board remained offline after connection.
ESPHome documentation revealed that most ESP32 models only support 2.4GHz Wi-Fi. Adjusting the Wi-Fi settings resolved the issue.
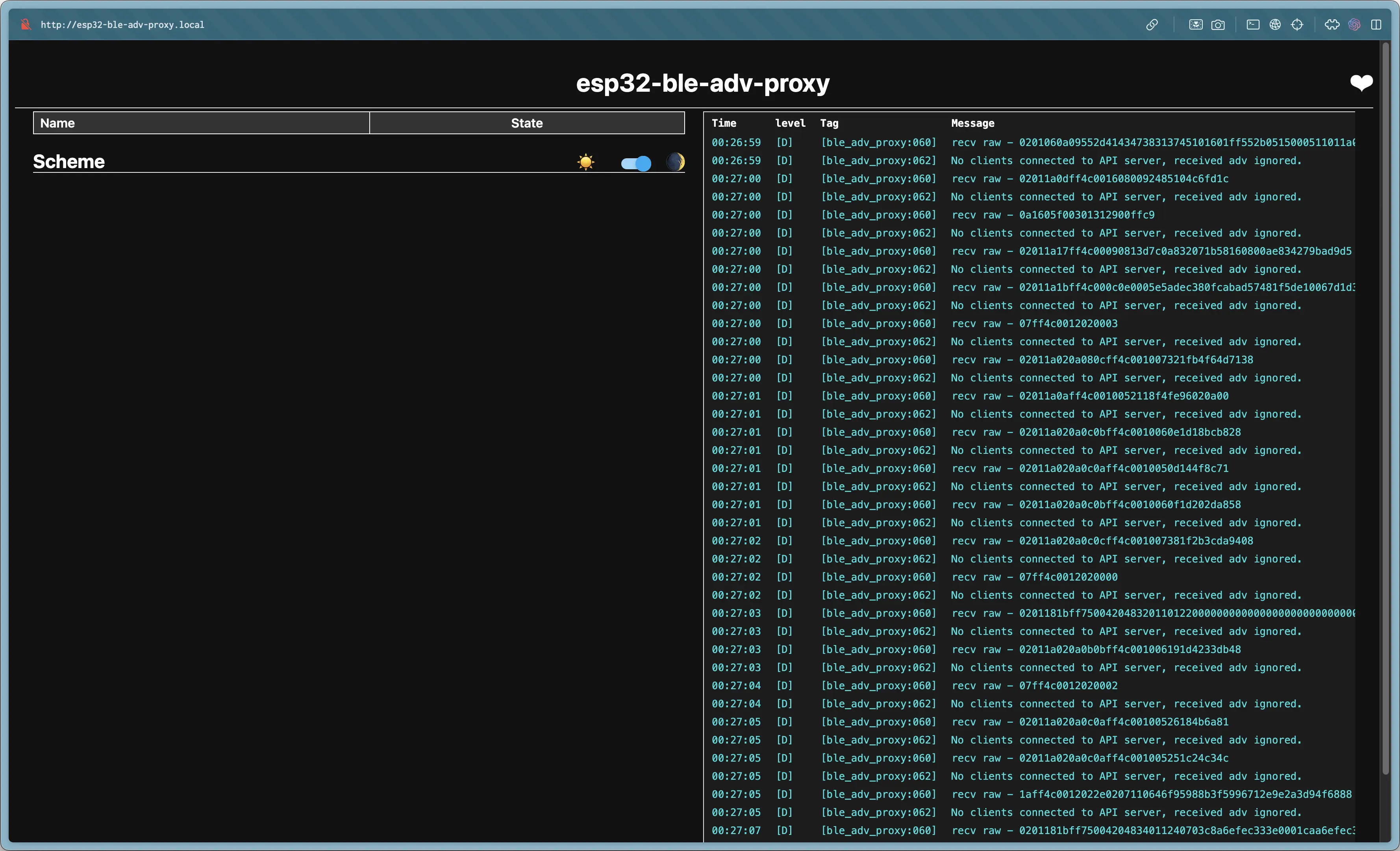
The ESP32 successfully connected to ble_adv_proxy. The Debug webpage showed it receiving Bluetooth signals from the environment.
3.2 ESP32 Home Assistant Integration: mDNS Resolution
The next step was integrating ESPHome with Home Assistant for ha-ble-adv to utilize the ble_adv_proxy.
ESPHome documentation indicated automatic discovery of the ESP32 device. However, the third challenge emerged: ESP32 addition failed.
Automatic discovery failed, and manual addition using the .local address also failed.
I attempted troubleshooting: Would using the IP address directly work?
Given the Docker deployment, the container might not resolve the ESP32’s .local address. I added extra_hosts to the Home Assistant Docker configuration:
extra_hosts:
- "esp32.local:192.168.50.66" # Map esp32.local to its IP address
Note: The automatic discovery failure indicated a deeper issue - mDNS service discovery protocol malfunction. This is a common issue in Docker deployments and affected subsequent operations.
After restarting Home Assistant, the device connected successfully using the .local address.
3.3 ha-ble-adv Configuration
With successful device addition, ha-ble-adv recognized the ESP32 as a Bluetooth adapter.
The fourth challenge appeared: ha-ble-adv configuration page inaccessible.
Debug logs showed a Python code error. After extensive troubleshooting, I filed an issue.
The author responded quickly and fixed the error.
After updating ha-ble-adv, I successfully accessed the configuration page and configured the Bluetooth ceiling light.
First milestone achieved: controlling the ceiling light via the ESP32 Bluetooth device!
This enabled Home Assistant control of the light’s power state and brightness.
IV. Final Challenge: HomeKit Bridge Integration
The final step was adding the HomeKit Bridge to integrate the light into Apple’s HomeKit ecosystem.
I expected this to be straightforward - enable the HomeKit Bridge component and add it in the Home app.
The final and most challenging obstacle appeared: HomeKit Bridge addition failed. This issue persisted for three days.
I researched extensively, consulting community posts and documentation. The problem pointed to network configuration. I investigated:
Docker’snetwork_modesettings- mDNS network configurations
- HomeKit network requirements
- Wi-Fi network settings
I attempted reinstalling Home Assistant and adjusting various Docker configurations.
Many users reported similar network issues in Docker environments, particularly with mDNS and HomeKit.
V. Solution: Native Deployment
I decided to remove Docker and deploy Home Assistant natively on macOS.
The results were immediate:
Home Assistantautomatically recognized and enabled themacOShost’s Bluetooth adapterHome Assistantautomatically discovered theESP32after ESPHome connection
Each step proceeded smoothly, with results matching expectations.
Finally, adding the HomeKit Bridge to HomeKit succeeded! 🎉
I can now control the ceiling light through the iPhone’s “Home” app or via Siri! Power control and brightness adjustment work as expected.
Final Implementation Demo
VI. Summary
Despite challenges, I successfully integrated the “non-smart” ceiling light into HomeKit using an ESP32 (25 RMB), saving approximately 100 RMB compared to the Mi Home version. This solution provided both technical value and cost efficiency.
Limitations:
The ble-adv solution has several limitations:
- Requires continuous
Home Assistantoperation - Requires persistent
ESP32connection - Cannot track current state - e.g., if the light is turned off via remote, the phone app still shows it as on